Write the Equation for the Reaction That Occurs When Methanol Is Dissolved in Water
Practice Test - MCQs test series for Term 2 Exams
LAKHMIR SINGH AND MANJIT KAUR Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise 18
Question 1
Why is respiration considered an exothermic process?
Solution 1
Respiration is an exothermic process because energy is produced during this process.
Question 2
On what basis is a chemical equation balanced?
Solution 2
A balanced chemical equation has equal number of atoms of different elements in the reactants and products.
Question 3
What happens chemically when quicklime is added to water filled in a bucket?
Solution 3
When quicklime is added to water, it forms slaked lime along with evolution of heat. There will be a rise in temperature of the bucket.
Question 4
Why should magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Solution 4
Magnesium ribbon should be cleaned before burning in air to remove the protective layer of basic magnesium carbonate from its surface.
Question 5
State whether the following statement is true or false:
A chemical equation can be balanced easily by altering the formula of a reactant or product.
Solution 5
False.
Question 6
What is wrong with the following chemical equation?
Mg + O ![]() MgO
MgO
Correct and balance it.
Solution 6
Oxygen should be in molecular form, O2
2Mg + O2 ![]() 2MgO
2MgO
Question 7
What does the symbol (aq) represent in a chemical equation?
Solution 7
The symbol (aq) represents aqueous solution in a chemical equation.
Question 8
Why is photosynthesis considered an endothermic reaction?
Solution 8
Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction because sunlight energy is absorbed by green plants during this process.
Question 9
How will you indicate the following effects in a chemical equation?
(a) A solution made in water
(b) Exothermic reaction
(c) Endothermic reaction
Solution 9
(a) Aqueous solution is indicated by the symbol 'aq'.
(b) An exothermic reaction is indicated by writing "+Heat" or "+Heat energy" or "+Energy" on the products side of an equation.
(c) An endothermic reaction is indicated by writing "+Heat" or "+Heat energy" or "+Energy" on the reactants side of an equation.
Question 10
Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance the equations:
(a) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
(b) Phosphorus burns in oxygen to give phosphorus pentoxide.
(c) Carbon disulphate burns in air to give carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide.
(d) Aluminium metal replaces iron from ferric oxide, Fe2O3, giving aluminium oxide and iron.
(e) Barium chloride reacts with zinc sulphate to give zinc chloride and barium sulphate.
Solution 10
(a) 2H2S + 3O2 ![]() 2H2O + 2SO2
2H2O + 2SO2
(b) P4 + 5O2 ![]() 2P2O5
2P2O5
(c) CS2 + 3O2 ![]() CO2 + 2SO2
CO2 + 2SO2
(d) 2Al + Fe2O3 ![]() Al2O3 + 2Fe
Al2O3 + 2Fe
(e) BaCl2 + ZnSO4 ![]() ZnCl2 + BaSO4
ZnCl2 + BaSO4
Question 11
Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions:
(a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide ![]() Calcium carbonate + Water
Calcium carbonate + Water
(b) Aluminium + Copper chloride ![]() Aluminimun chloride + Copper
Aluminimun chloride + Copper
Solution 11
(a) Ca(OH)2 + CO2 ![]() CaCO3 + H2O
CaCO3 + H2O
(b) 2Al + 3CuCl2 ![]() 2AlCl3 + 3Cu
2AlCl3 + 3Cu
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise 19
Question 12
Complete and balance the following equations:
(a) NaOH + ______ ![]() Na2SO4 + H2O
Na2SO4 + H2O
(b) Ca(OH)2 + _______ ![]() CaCO3 + H2O
CaCO3 + H2O
Solution 12
(a) 2NaOH + H2SO4 ![]() Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(b) Ca(OH)2 + CO2 ![]() CaCO3 + H2O
CaCO3 + H2O
Question 13
Correct and balance the following equations:
(i) Ca + H2O ![]() CaOH + H
CaOH + H
(ii) N + H ![]() NH3
NH3
Solution 13
(i) Ca + 2H2O ![]() Ca(OH)2 + H2
Ca(OH)2 + H2
(ii) N2 + 3H2 ![]() 2NH3
2NH3
Question 14
Write complete balanced equations for the following reactions:
(a) Calcium (solid) + Water (liquid) ![]() Calcium hydroxide (solution) + Hydrogen (gas)
Calcium hydroxide (solution) + Hydrogen (gas)
(b) Sulphur dioxide (gas) + Oxygen (gas) ![]() Sulphur trioxide (gas)
Sulphur trioxide (gas)
Solution 14
(a) Ca (s) + 2H2O (l) ![]() Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
(b) 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ![]() 2SO3 (g)
2SO3 (g)
Question 15
Balance the following equations:
(i) Na + O2 ![]()
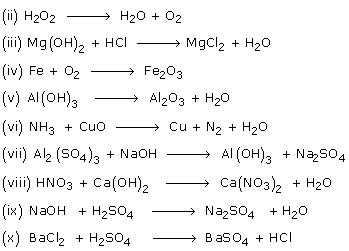
Solution 15
(i) 4Na + O2 ![]() 2Na2O
2Na2O
(ii) 2H2O2 ![]() 2H2O + O2
2H2O + O2
(iii) Mg(OH)2 + 2HCl ![]() MgCl2 + 2H2O.
MgCl2 + 2H2O.
(iv) 4Fe + 3O2 ![]() 2Fe2O3
2Fe2O3
(v) 2Al(OH)3 ![]() Al2O3 + 3H2O
Al2O3 + 3H2O
(vi) 2NH3 + 3CuO ![]() 3Cu + N2 + 3H2O
3Cu + N2 + 3H2O
(vii) Al2(SO4)3 + 6NaOH ![]() 2Al(OH)3 + 3Na2SO4
2Al(OH)3 + 3Na2SO4
(viii) 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 ![]() Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
(ix) 2NaOH + H2SO4 ![]() Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(x) BaCl2 + H2SO4 ![]() BaSO4 + 2HCl
BaSO4 + 2HCl
Question 16
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words:
(a) Chemical equations are balanced to satisfy the law of _______.
(b) A solution made in water is known as an ____ solution and indicated by the symbol _______.
Solution 16
(a) Conservation of mass
(b) Aqueous; (aq)
Question 17
(a) Give one example of a chemical reaction.
(b) State two characteristics of the chemical reaction which takes place when dilute sulphuric acid is poured over zinc granules.
(c) Give two characteristics of the chemical reaction which occurs on adding potassium iodide solution to lead nitrate solution.
Solution 17
(a) Magnesium Ribbon is heated in the presence of air to form a white powder called magnesium oxide.
(b) When dilute sulphuric acid is poured over zinc granules (i) there will be a rise in temperature (ii) evolution of hydrogen gas.
(c) (i) A yellow precipitate is formed.
(ii) There will be a change in color (from colourless to yellow).
Question 18
(a) What is a chemical equation? Explain with the help of an example.
(b) Giving examples, state the difference between balanced and unbalanced chemical equations.
(c) Balance the following chemical equations:
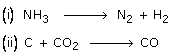
Solution 18
(a) The method of representing a chemical reaction with the help of symbols and formulae of substances involved in it is called a chemical equation.
Example: Zinc metal reacts with dilute sulphuric acid to form zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas. This equation is written as: Zn + H2SO4 ![]() ZnSO4 + H2
ZnSO4 + H2
(b) A balanced chemical equation has an equal number of atoms of different elements in the reactants and products. It has equal masses of various elements in the reactants and products.
Example: Zn + H2SO4 ![]() ZnSO4 + H2
ZnSO4 + H2
An unbalanced chemical equation has an unequal number of atoms of one or more elements in the reactants and products. It has unequal masses of various elements in the reactants and products.
Example: H2 + O2 ![]() H2O
H2O
(c) (i) 2NH3 ![]() N2 + 3H2 (ii) C + CO2
N2 + 3H2 (ii) C + CO2 ![]() 2CO
2CO
Question 19
When hydrogen is passed over copper oxide, copper and steam are formed. Write a balanced equation for this reaction and state which of the chemicals are:
(i) Elements
(ii) Compounds
(iii) Reactants
(iv) Products
(v) Metals
(vi) Non-metals
Solution 19
H2 + CuO ![]() Cu + H2O
Cu + H2O
(i) Elements : H2 and Cu
(ii) Compounds : CuO and H2O
(iii) Reactants: H2 and CuO
(iv) Products: Cu and H2O
(v) Metal: Cu
(vi) Non-metal: H2
Question 20
(a) What are the various ways in which a chemical equation can be made more informative? Give examples to illustrate your answer.
(b) Write balanced chemical equation from the following information:
An aqueous calcium hydroxide solution (lime water) reacts with carbon dioxide gas to produce a solid calcium carbonate precipitate and water.
Solution 20
(a) The various ways in which a chemical equation can be made more informative are :
(i) By indicating the physical states of the reactants and products. Example: Gaseous state is indicated by the symbol (g).
Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) ZnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
(ii) By indicating the heat changes taking place in the reaction. For xxample: An exothermic reaction is indicated by writing "+Heat" or "+Heat energy" or "+Energy" on the products side of an equation.
C (s) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + Heat
(iii) By indicating the "conditions" under which the reaction takes place.
Example: Delta stands for heat which is written over the arrow of the equation.
(b) Ca(OH)2 (aq) + CO2 (g) ![]() CaCO3 (s) + H2O (l)
CaCO3 (s) + H2O (l)
Question 21
(a) What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
(b) Aluminium burns in chlorine to form aluminium chloride (AlCl3). Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
(c) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
Solution 21
(a) A balanced chemical equation has an equal number of atoms of different elements in the reactants and products. It has equal masses of various elements in the reactants and products. A chemical equation should be balanced to satisfy the law of conservation of chemical reactions.
(b) 2Al + 3Cl2 ![]() 2AlCl3
2AlCl3
(c) 2K + 2H2O ![]() 2KOH + H2
2KOH + H2
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise 20
Question 22
(a) Explain, with example, how the physical states of the reactants and products can be shown in a chemical equation.
(b) Balance the following equation and add state symbols:
Zn + HCl ![]() ZnCl2 + H2
ZnCl2 + H2
(c) Convey the following information in the form of a balanced chemical equation:
"An aqueous solution of ferrous sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide to form a precipitate of ferrous hydroxide and sodium sulphate remains in solution."
Solution 22
(a) The physical states of the reactants and products are shown by putting the "state symbols" in an equation.
For example: Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) ![]() ZnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
ZnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
(b) Zn (s) + 2HCl (aq) ![]() ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
(c) FeSO4(aq) + 2NaOH (aq) ![]() Fe(OH)2 (s) + Na2SO4 (aq)
Fe(OH)2 (s) + Na2SO4 (aq)
Question 23
Write any two observations in an activity which may suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. Give an example in support of your answer.
Solution 23
(i) Evolution of gas.
For example: When sodium carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, carbon dioxide gas is evolved.
(ii) Formation of a precipitate.
For example: When potassium iodide solution is added to a solution of lead nitrate, yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed.
Question 24
(a) Aluminium hydroxide reacts with sulphuric acid to form aluminium sulphate and water. Write a balanced equation for this reaction.
(b) Balance the following chemical equation:
![]()
Solution 24
(a) 2Al(OH)3 + 3H2SO4 ![]() Al2(SO4)3 + 6H2O
Al2(SO4)3 + 6H2O
(b) MnO2 + 4HCl ![]() MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
Question 25
Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions, and add the state symbols:
(a) Magnesium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce magnesium chloride, carbon dioxide and water.
(b) Sodium hydroxide reacts with sulphuric acid to produce sodium sulphate and water.
Solution 25
(a) MgCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) ![]() MgCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
MgCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
(b) 2NaOH (aq) + H2SO4 (aq) ![]() Na2SO4 (aq) + 2H2O (l)
Na2SO4 (aq) + 2H2O (l)
Question 26
Carbon monoxide reacts with hydrogen under certain conditions to form methanol (CH3OH). Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction indicating the physical states of reactants and product as well as the conditions under which this reaction takes place.
Solution 26

The conditions for this reaction to take place are: a pressure of 300 atmospheres (written as 300 atm), a temperature of 300oC, and a catalyst which is a mixture of zinc oxide and chromium oxide (ZnO + CrO3).
Question 27
(a) Potassium chlorate (KClO3) on heating forms potassium chloride and oxygen. Write a balanced equation for this reaction and indicate the evolution of gas.
(b) Rewrite the following information in the form of a balanced chemical equation:
Magnesium burns in carbon dioxide to form magnesium oxide and carbon.
Solution 27
(a) 2KClO3 (s) ![]() 2KCl (s) + 3O2 (g)
2KCl (s) + 3O2 (g)
(b) 2Mg + CO2 ![]() 2MgO + C
2MgO + C
Question 28
(a) Substitute formulae for names and balance the following equations:
Calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce calcium chloride, water and carbon dioxide gas.
(b) Write balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reaction:
Sodium hydroxide solution reacts with hydrochloric acid solution to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Solution 28
(a) CaCO3 + 2HCl ![]() CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
(b) NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) ![]() NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
Question 29
Ammonia reacts with oxygen to form nitrogen and water. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. Add the state symbols for all the reactants and products.
Solution 29
4NH3 (g) + 3O2 (g) ![]() 2N2 (g) + 6H2O (l)
2N2 (g) + 6H2O (l)
Question 30
Write a balanced chemical equation for the process of photosynthesis giving the physical states of all the substances involved and the conditions of the reaction.
Solution 30
6CO2 (g) + 6H2O (l) ![]() C6H12O6 (aq) + 6O2 (g)
C6H12O6 (aq) + 6O2 (g)
Carbon dioxide Water Glucose Oxygen
Question 31
Translate the following statement into chemical equation and then balance it:
Barium chloride solution reacts with aluminium sulphate solution to form a perciptate of barium sulphate and aluminium chloride solution.
Solution 31
3BaCl2 (aq) + Al2(SO4)3 (aq) ![]() 3BaSO4 (s) + 2AlCl3 (aq)
3BaSO4 (s) + 2AlCl3 (aq)
Question 32
When potassium nitrate is heated, it decomposes into potassium nitrite and oxygen. Write a balanced equation for this reaction and add the state symbols of the reactants and products.
Solution 32
2KNO3 (s) ![]() 2KNO2 (s) + O2 (g)
2KNO2 (s) + O2 (g)
Question 33
(a) What is meant by a chemical reaction? Explain with the help of an example.
(b) Give one example each of a chemical reaction characterised by:
(i) Evolution of a gas
(ii) Change in colour
(iii) Formation of a precipitate
(iv) Change in temperature
(v) Change in state.
Solution 33
(a) Chemical reactions are the processes in which new substances with new properties are formed.
For example: When magnesium ribbon is heated, it burns in air to form a white powder called magnesium oxide.
(b) (i) The chemical reaction between zinc and dilute sulphuric acid.
(ii) The chemical reaction between citric acid and purple coloured potassium permanganate solution is characterised by change in colour (from purple to colourless).
(iii) The chemical reaction between potassium iodide and lead nitrate is characterised by the formation of a yellow precipitate of lead iodide.
(iv) The reaction between quick lime and water to form slaked lime is characterised by a change in temperature.
(v) When wax is burned, then water and carbon dioxide are formed. Wax is a solid; water is a liquid whereas carbon dioxide is a gas.
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise 21
Question 34
(a) State the various characteristics of chemical reactions.
(b) State one characteristics each of the chemical reaction which takes place when:
(i) Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium carbonate
(ii) Lemon juice is added gradually to potassium permanganate solution
(iii) Dilute sulphuric acid is added to barium chloride solution
(iv) Quicklime is treated with water
(v) Wax is burned in the form of a candle
Solution 34
(a) The various characteristics of chemical reactions are:
(i) Evolution of a gas (ii) Formation of a precipitate (iii) Change in colour (iv) Change in temperature (v) Change in state.
(b) (i) Evolution of carbon dioxide gas (ii) Change in colour from purple to colourless (iii) Formation of white precipitate of barium sulphate (iv) Change in temperature (v) Change in state from solid to liquid and gas.
Question 35
(a) What do you understand by exothermic and endothermic reactions?
(b) Give one example of an exothermic reaction and one of an endothermic reaction.
(c) Which of the following are endothermic reactions and which are exothermic reactions?
(i) Burning of natural gas
(ii) Photosynthesis
(iii) Electrolysis of water
(iv) Respiration
(v) Decomposition of calcium carbonate
Solution 35
(a) Those reactions in which heat is evolved are known as exothermic reactions.
The reactions in which heat is absorbed are known as endothermic reactions.
(b) Example of exothermic reaction:
C (s) + O2 (g) ![]() CO2 + Heat
CO2 + Heat
Example of endothermic reaction:
N2 (g) + O2 (g) + Heat ![]() 2NO (g)
2NO (g)
(c) Endothermic reactions: Photosynthesis, Electrolysis of water, Decomposition of calcium carbonate.
Exothermic reactions: Burning of natural gas, Respiration.
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise 22
Question 46
When the solution of substance X is added to a solution of potassium iodide, then a yellow solid separates out from the solution.
(a) what do you think substance X is likely to be?
(b) Name the substance which the yellow solid consists of.
(c) Which characteristic of chemical reactions is illustrated by this example?
(d) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction which takes place. Mention the physical states of all the reactants and products involved in the chemical equation.
Solution 46
(a) Lead nitrate.
(b) Lead iodide.
(c) Formation of a precipitate.
(d) Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) ![]() PbI2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
PbI2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
Question 47
When water is added gradually to a white solid X, a hissing sound and a lot of heat is produced forming a product Y. A suspension of Y in water is applied to the walls of a house during white washing. A clear solution of Y is also used for testing carbon dioxide gas in the laboratory.
(a) What could be solid X? Write its chemical formula.
(b) What could be product Y? write its chemical formula.
(c) What is the common name of the solution of Y which is used for testing carbon dioxide gas?
(d) Write chemical equation of the reaction which takes place on adding water to solid X.
(e) Which characteristics of chemical reactions is illustrate by this example?
Solution 47
(a) Calcium oxide, CaO.
(b) Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2
(c) Lime water.
(d) CaO + H2O ![]() Ca(OH)2
Ca(OH)2
(e) Change in temperature.
Question 48
When metal X is treated with a dilute acid Y, then a gas Z is evolved which burns readily by making a little explosion.
(a) Name any two metals which can behave like metal X.
(b) Name any two acids which can behave like acid Y.
(c) Name the gas Z.
(d) Is the gas Z lighter than or heavier than air?
(e) Is the reaction between metal X and dilute acid Y exothermic or endothermic?
(f) By taking a specific example of metal X and dilute acid Y, write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction which takes place. Also indicate physical states of all the reactants and products.
Solution 48
(a) Zinc and Iron.
(b) Dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute sulphuric acid.
(c) Hydrogen.
(d) Lighter than air.
(e) Exothermic.
(f) Suppose metal X is zinc (Zn) and acid Y is dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) ;
Zn (s) + 2HCl (aq) ![]() ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Question 49
A solid substance P which is very hard is used in the construction of many buildings, especially flooring. When substance P is heated strongly, it decomposes to form another solid Q and a gas R is given out. Solid Q reacts with water with the release of a lot of heat to form a substance S. When gas R is passed into a clear solution of substance S, then a white precipitate of substance T is formed. The substance T has the same chemical composition as starting substance P.
(a) What is substance P? Write its common name as well as chemical formula.
(b) What is substance Q?
(c) What is gas R?
(d) What is substance S? what is its clear solution known as?
(e) What is substance T? Name any two natural forms in which substance T occurs in nature.
Solution 49
(a) Calcium carbonate (limestone), CaCO3
(b) Calcium oxide, CaO
(c) Carbon dioxide, CO2
(d) Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2; Lime water.
(e) Calcium carbonate; Limestone and Marble.
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise 23
Question 50
A silvery-white metal X taken in the form of ribbon, when ignited, burns in air with a dazzling white flame to form a white powder Y. When water is added to powder Y, it dissolves partially to form another substance Z.
(a) What could metal X be?
(b) What is powder Y?
(c) With which substance metal X combines to form powder Y?
(d) What is substance Z? Name one domestic use of substance Z.
(e) Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction which takes place when metal X burns in air to form powder Y.
Solution 50
(a) Magnesium, Mg.
(b) Magnesium oxide, MgO
(c) Oxygen (of air), O2
(d) Magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2; Used as antacid to relieve indigestion
(e) 2Mg + O2 ![]() 2MgO
2MgO
Question 51
A metal X forms a salt XSO4. The salt XSO4 forms a clear solution in water which reacts with sodium hydroxide solution to form a blue precipitate Y. Metal X is used in making electric wires and alloys like brass.
(a) What do you think metal X could be?
(b) Write the name, formula and colour of salt XSO4.
(c) What is the blue precipitate Y?
(d) Write a chemical equation of the reaction which takes place when salt XSO4 reacts with sodium hydroxide solution. Give the state symbols of all the reactants and products which occur in the above equation.
Solution 51
(a) Copper, Cu.
(b) Copper sulphate, CuSO4, Blue colour.
(c) Copper hydroxide, Cu(OH)2
(d) CuSO4 (aq) + 2NaOH (aq) ![]() Cu(OH)2 (s) + Na2S04 (aq)
Cu(OH)2 (s) + Na2S04 (aq)
Question 52
The metal M reacts vigorously with water to form a solution S and a gas G. The solution S turns red litmus to blue whereas gas G, which is lighter than air, burns with a pop sound. Metal M has a low melting point and it is used as a coolant in nuclear reactors.
(a) What is metal M?
(b) What is solution S? Is it acidic or alkaline?
(c) What is gas G?
(d) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction which takes place when metal M reacts with water.
(e) Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Solution 52
(a) Sodium, Na.
(b) Sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH solution), Alkaline. (c) Hydrogen, H2
(d) 2Na + 2H2O ![]() 2NaOH + H2
2NaOH + H2
(e) Exothermic.
Question 53
When a mixture of gases X and Y is compressed to 300 atm pressure and then passed over a catalyst consisting of a mixture of zinc oxide and chromium oxide (heated to a temperature of 300oC), then an organic compound Z having the molecular formula CH4O is formed. X is a highly poisonous gas which is formed in appreciable amounts when a fuel burns in a limited supply of air; Y is a gas which can be made by the action of a dilute acid on an active metal; and Z is a liquid organic compound which can react with sodium metal to produce hydrogen gas.
(a) What are X, Y and Z?
(b) Write a balance chemical equation of the reaction which takes place when X and Y combine to form Z. Indicate the conditions under which the reaction occurs.
Solution 53
(a) X is carbon monoxide gas (CO); Y is hydrogen gas (H2) ; Z is methanol (or Methyl alcohol) (CH3OH)
(CH40 = CH3OH)
(b) Formation of Z:

The conditions for this reaction to take place are: a pressure of 300 atmospheres (written as 300 atm), a temperature of 300oC, and a catalyst which is a mixture of zinc oxide and chromium oxide (ZnO + CrO3).
Question 54
The white solid compound A decomposes quite rapidly on heating in the presence of a black substance X to form a solid compound B and a gas C. When an aqueous solution of compound B is reacted with silver nitrate solution, then a white precipitate of silver chloride is obtained alongwith potassium nitrate solution. Gas C does not burn itself but helps burn things.
(a) what is compound A?
(b) What is compound B?
(c) What is gas C?
(d) What do you think is the black substance X? What is its function?
(e) What is the general name of substance like X?
Solution 54
(a) Potassium chlorate, KClO3
(b) Potassium chloride, KCl
(c) Oxygen, O2
(d) Manganese dioxide, MnO2; It acts as a catalyst in the decomposition of potassium chlorate to form oxygen gas
(e) Catalysts
Question 55
Gas A, which is the major cause of global warming, combines with hydrogen oxide B in nature in the presence of an environmental factor C and a green material D to form a six carbon organic compound E and a gas F. The gas F is necessary for breathing.
(a) What is gas A?
(b) What is the common name B?
(c) What do you think could be C?
(d) What is material D? Where is it found?
(e) Name the organic compound E.
(f) What is gas F? Name the natural process during which it is released.
Solution 55
(a) Carbon dioxide, CO2
(b) Water, H2O
(c) Sunlight.
(d) Chlorophyll; Green leaves of plants.
(e) Glucose, C6H12O6
(f) Oxygen; Photosynthesis.
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise 45
Question 1
What type of reaction is represented by the digestion of food in our body?
Solution 1
Decomposition reaction.
Question 2
Name the various types of chemical reactions.
Solution 2
The various types of chemical reactions are:
(i) Combination reactions.
(ii) Decomposition reaction.
(iii) Displacement reaction.
(iv) Double displacement reaction.
(v) Oxidation and reduction reactions.
Question 3
Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is kept immersed in it?
Solution 3
The colour of copper sulphate solution changes when iron nail is kept immersed in it due to the displacement reaction taking place between iron and copper leading to formation of iron sulphate.
Question 4
Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reaction:
Zinc + Silver nitrate Zinc nitrate + Silver
Solution 4
Zn + 2AgNO3 Zn(NO3)2 + 2Ag
Question 5
Which term is used to indicate the development of unpleasant smell and taste in fat and oil containing foods due to aerial oxidation (when they are kept exposed for a considerable time)?
Solution 5
Rancidity.
Question 6
What is the general name of the chemicals which are added to fat and oil containing foods to prevent the development of rancidity?
Solution 6
Anti-oxidants.
Question 7
State an important use of decomposition reactions.
Solution 7
The digestion of food in the body is an example of decomposition reaction.
Question 8
What are anti-oxidants? Why are they added to fat and oil containing foods?
Solution 8
Anti-oxidant is a substance which prevents oxidation. They are added to fat and oil containing foods so that they do not get oxidized easily and hence do not turn rancid.
Question 9
Explain why, food products containing fats and oils (like potato chips) are packaged in nitrogen.
Solution 9
Food products containing fats and oils are packaged in nitrogen so that there is no oxygen to cause oxidation of food and make it rancid.
Question 10
Give one example of a decomposition reaction which is carried out:
(a) With electricity
(b) By applying heat
Solution 10
(a) When fused sodium chloride is decomposed by passing electricity, sodium metal is obtained.
(b) When lead nitrate is heated strongly, it breaks down to form lead monoxide, nitrogen dioxide and oxygen.
Question 11
What type of chemical reaction is used to extract metals from their naturally compounds like oxides or chlorides?
Solution 11
Decomposition reactions (carried out by electricity).
Question 12
Name two anti-oxidants which are usually added to fat and oil containing foods to prevent rancidity.
Solution 12
BHA (Butylated Hydroxy Anisole) and BHT (Butylated Hydroxy Toluene).
Question 13
Write one equation each for the decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of (a) heat, (b) light, and (c) electricity.
Solution 13
(a) Decomposition reaction where heat is supplied for energy:
(b) Decomposition reaction where light is supplied for energy:
(c) Decomposition reaction where electricity is supplied for energy:
Question 14
In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Solution 14
2AgNO3 (aq) + Cu (s) ![]() Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag (s)
Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag (s)
Question 15
What type of reactions are represented by the following equations?
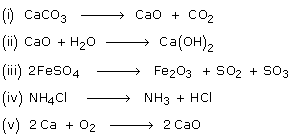
Solution 15
(i) Decomposition.
(ii) Combination.
(iii) Decomposition.
(iv) Decomposition.
(v) Combination.
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise 46
Question 16
What type of chemical reaction stake place when:
(a) A magnesium wire is burnt in air?
(b) Lime-stone is heated?
(c) Silver bromide is exposed to sunlight?
(d) Electricity is passed through water?
(e) Ammonia and hydrogen chloride are mixed?
Solution 16
(a) Combination.
(b) Decomposition.
(c) Decomposition.
(d) Decomposition.
(e) Combination.
Question 17
What type of chemical reactions are represented by the following equations?
Solution 17
(i) Displacement reaction.
(ii) Combination reaction.
(iii) Decomposition reaction.
(iv) Double displacement reaction.
(v) Displacement reaction.
Question 18
Balance the following chemical equations:
Solution 18
Question 19
Which of the following is a combination and which a displacement reaction.
Solution 19
(a) Displacement reaction.
(b) Combination reaction.
Question 20
What type of reactions are represented by the following equations?
Solution 20
(a) Combination reaction.
(b) Displacement reaction.
(c) Displacement reaction.
(d) Decomposition reaction.
(e) Double displacement reaction.
Question 21
In the following reaction between lead sulphide and hydrogen peroxide:
(a) Which substance is reduced?
(b) Which substance is oxidized?
Solution 21
Question 22
Identify the component oxidized in the following reaction:
Solution 22
H2S
Question 23
When SO2 gas is passed through saturated solution of H2S, the following reaction occurs:
In this reaction, which substance is oxidized and which one is reduced?
Solution 23
Substance oxidised: H2S
Substance reduced: SO2
Question 24
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words:
(a) The addition of oxygen to a substance is called ______ whereas removal of oxygen is called ______.
(b) The addition of hydrogen to a substance is called ______ whereas removal of hydrogen is called ______.
(c) Anti-oxidants are often added to fat containing foods to prevent ______ due to oxidation
Solution 24
(a) Oxidation; reduction.
(b) Reduction; oxidation.
(c) Rancidity.
Question 25
What is an oxidation reaction? Identify in the following reaction (i) the substance oxidized, and (ii) substance reduced:
Solution 25
Oxidation Reaction: The addition of oxygen (or removal of hydrogen) to a substance is called oxidation.
(i) C (ii) ZnO
Question 26
(a) What is a redox reaction? Explain with an example.
(b) When a magnesium ribbon burns in air with a dazzling flame and forms a white ash, is magnesium oxidised or reduced? Why?
(c) In the reaction represented by the equation:
(i) name the substance oxidized (ii) name the oxidizing agent
(ii) name the substance reduced (iv) name the reducing agent
Solution 26
(a) The oxidation and reduction reactions occurring together are called a redox reaction. Example:
In this reaction, copper oxide is being reduced to copper whereas hydrogen is being oxidised to water.
(b) Magnesium is oxidised as addition of oxygen to magnesium takes place leading to formation of magnesium oxide.
(c) (i) HCl
(ii) MnO2
(iii) MnO2
(iv) HCl
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise 47
Question 27
(a) Define a combination reaction.
(b) Give one example of a combination reaction which is also exothermic.
(c) Give one example of a combination reaction which is also endothermic.
Solution 27
(a) Those reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a single substance is called a combination reaction.
(b) C (s) + O2 (g) ![]() CO2 + Heat
CO2 + Heat
(c) N2 (g) + O2 (g) + Heat ![]() 2NO (g)
2NO (g)
Question 28
(a) Give an example of an endothermic reaction?
(b) Is oxidation an exothermic or an endothermic reaction?
(c) Explain, by giving an example, how oxidation and reduction processed side by side.
Solution 28
(a) C (s) + O2 (g) ![]() CO2 + Heat
CO2 + Heat
(b) Oxidation reaction is an exothermic reaction.
(c)
In this reaction, copper oxide is being reduced to copper whereas hydrogen is being oxidised to water.
Question 29
(a) What is the colour of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this colour change after heating?
(b) Name the product formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this change?
Solution 29
(a) The colour of ferrous sulphate is green. It changes to brown after heating.
(b) The product formed is ferric oxide. This is a decomposition reaction.
Question 30
What is a decomposition reaction? Give an example of a decomposition reaction. Describe an activity to illustrate such a reaction by heating.
Solution 30
Those reactions in which a compound splits up into two or more simpler substances is called a decomposition reaction.
When calcium carbonate is heated, it decomposes to give calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
Activity: When potassium chlorrate is heated in the presence of manganese dioxide catalyst, it decomposes to give potassium chloride and oxygen:
This decomposition takes place in the presence of heat and catalyst. In this decomposition reaction, a single compound, potassium chlorate, is splitting up into two simpler substances, potassium chloride and oxygen. This decomposition reaction is used for preparing oxygen gas in the laboratory.
Question 31
Zinc oxide reacts with carbon, on heating, to form zinc metal and carbon monoxide. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. Name (i) oxidising agent, and (ii) reducing agent, in this reaction.
Solution 31
ZnO + C ![]() Zn + CO
Zn + CO
(i) Zinc oxide.
(ii) Carbon.
Question 32
Give one example of an oxidation-reduction reaction which is also:
(a) A combination reaction
(b) A displacement reaction
Solution 32
(a)
(b)
Question 33
(a) What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
(b) What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain giving an example.
Solution 33
(a) Those reactions in which one element takes the place of another element in a compound, are known as displacement reactions.
Equation: CuSO4 (aq) + Zn (s) ![]() ZnSO4 + Cu
ZnSO4 + Cu
Those reactions in which two compounds react by an exchange of ions to form two new compounds are called double displacement reactions.
Equation: AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) ![]() AgCl (s)+ NaNO3 (aq)
AgCl (s)+ NaNO3 (aq)
(b) Any reaction in which an insoluble solid (called precipitate) is formed that separates from the solution is called a precipitation reaction.
Example: The reaction between barium chloride and sodium sulphate solution to form a white barium sulphate precipitate (alongwith sodium chloride solution) is an example of a precipitation reaction.
Question 35
(a) Define the following in terms of gain or loss of hydrogen with one example each:
(i) oxidation (ii) reduction
(b) When a magnesium ribbon is heated, it burns in air to form magnesium oxide. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. Name (i) substance oxidised, and (ii) substance reduced.
Solution 35
(a) (i) H2S + Cl2 ![]() S + 2HCl
S + 2HCl
In this reaction, H2S is changing into S. That is, Hydrogen is being removed from hydrogen sulphide. Now, by definition, the removal of hydrogen from a compound is called oxidation, so, we can say that hydrogen sulphide is being oxidised to sulphur. On the other hand, Cl2 is changing into HCl. That is, hydrogen is being added to chlorine. By definition, the addition of hydrogen to a substance is called reduction, so we can say that chlorine is being reduced to hydrogen chloride.
(b) 2Mg + O2 ![]() 2MgO
2MgO
(i) Mg (ii) O2
Question 36
What is meant by (a) displacement reaction, and (b) double displacement reaction? Explain with the help of one example each.
Solution 36
(a) Those reactions in which one element takes the place of another element in a compound, are known as displacement reactions.
Example: CuSO4 (aq) + Zn (s) ![]() ZnSO4 + Cu
ZnSO4 + Cu
When a strip of zinc metal is placed in copper sulphate solution, then zinc sulphate solution and copper are obtained. In this reaction, zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate compound so that copper is set free. The blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades due to the formation of zinc sulphate.
(b) Those reactions in which two compounds react by an exchange of ions to form two new compounds are called double displacement reactions.
Example: AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) ![]() AgCl (s)+ NaNO3 (aq)
AgCl (s)+ NaNO3 (aq)
When silver nitrate solution is added to sodium chloride solution, then a white precipitate of silver chloride is formed alongwith sodium nitrate solution. In this reaction, two compounds, silver nitrate and sodium chloride, react to form two new compounds, silver chloride and sodium nitrate.
Question 37
(a) Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Explain with equations of these reactions.
(b) Express the following facts in the form of a balanced chemical equation:
"When a strip of copper metal is placed in a solution of silver nitrate, metallic silver is precipitated and a solution containing copper nitrate is formed."
Solution 37
Those reactions in which a compound splits up into two or more simpler substances are known as decomposition reactions.
Example: When calcium carbonate is heated, it decomposes to give calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
They are called opposite of combination reactions because in a combination reaction, two or more substances combine to form a single substance.
Example: Magnesium and oxygen combine, when heated, to form magnesium oxide.
(b) Cu (s) + 2AgNO3 (aq) ![]() Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag (s)
Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag (s)
Question 38
(a) What happens when a piece of iron metal is placed in copper sulphate solution? Name the type of reaction involved.
(b) Write balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reaction:
Barium chloride solution reacts with sodium sulphate solution to give insoluble barium sulphate and a solution of sodium chloride.
Solution 38
(a) When a piece of iron metal is placed in copper sulphate solution, then magnesium sulphate solution and copper metal are formed. This is a type of displacement reaction.
(b)
Question 39
In the reaction represented by the following equation:
(a) Name the substance oxidised
(b) Name the substance reduced
(c) Name the oxidising agent
(d) Name the reducing agent
Solution 39
(a) H2
(b) CuO
(c) CuO
(d) H2
Question 40
What happens when silver nitrate solution is added to sodium chloride solution?
(a) Write the equation for the reaction which takes place.
(b) Name the type of reaction involved.
Solution 40
When silver nitrate solution is added to sodium chloride solution, then a white precipitate of silver chloride is formed alongwith sodium nitrate solution.
(a) AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) ![]() AgCl (s)+ NaNO3 (aq)
AgCl (s)+ NaNO3 (aq)
(b) Double displacement reaction.
Question 41
What happens when silver chloride is exposed to sunlight? Write a chemical equation for this reaction. Also give one use of such a reaction.
Solution 41
When silver chloride is exposed to light, it decomposes to form silver metal and chlorine gas.
This reaction is used in black and white photography.
Question 42
What happens when a zinc strip is dipped into a copper sulphate solution?
(a) Write the equation for the reaction that takes place.
(b) Name the type of reaction involved.
Solution 42
When a strip of zinc metal is placed in copper sulphate solution, then zinc sulphate solution and copper are obtained.
(b) Displacement reaction.
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise 48
Question 43
(a) Explain the term "corrosion" with an example. Write a chemical equation to show the process of corrosion of iron.
(b) What special name is given to the corrosion of iron?
(c) What type of chemical reaction is involved in the corrosion of iron?
(d) Name any three objects (or structures) which are gradually damaged by the corrosion of iron and steel.
Solution 43
(a) Corrosion is the process in which metals are eaten up gradually by the action of air, moisture or a chemical (such as an acid) on their surface. Rusting of iron metal is the most common form of corrosion.
During the corrosion of iron, iron metal is oxidised by the oxygen of air in the presence of water (moisture) to form hydrated iron oxide called rust.
(b) Rusting.
(c) Oxidation.
(d) Railings, car bodies and bridges.
Question 44
(a) Explain the term "rancidity". What damage is caused by rancidity?
(b) What type of chemical reaction is responsible for causing rancidity?
(c) State and explain the various methods for preventing or retarding rancidity of food.
Solution 44
(a) The condition produced by aerial oxidation of fats and oils in foods marked by unpleasant smell and taste is called rancidity. It spoils the food materials prepared in fats and oils which have been kept for a considerable time and makes them unfit for eating.
(b) Oxidation.
(c) (i) Rancidity can be prevented by adding anti-oxidants to foods containing fats and oils.
(ii) It can be prevented by packaging fat and oil containing foods in nitrogen gas.
(iii) Rancidity can be retarded by keeping food in a refrigerator.
(iv) Rancidity can be prevented by storing food in air-tight containers.
(v) Storing foods away from light can also prevent rancidity.
Question 45
(a) What happens when an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of barium chloride?
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction which takes place.
(c) State the physical conditions of reactants in which the reaction will not take place.
(d) Name the type of chemical reaction which occurs.
(e) Give one example of another reaction which is of the same type as the above reaction.
Solution 45
(a) When barium chloride solution is added to sodium sulphate solution, then a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed alongwith sodium chloride solution.
(b)
(c) Solid sodium sulphate and Solid barium chloride
(d) Double displacement reaction.
(e) Double displacement reaction between silver nitrate solution and sodium chloride solution forms a white precipitate of silver chloride and sodium nitrate solution.
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise 49
Question 58
When a green iron salt is heated strongly, its colour finally changes to brown and odour of burning sulphur is given out.
(a) Name the iron salt.
(b) Name the type of reaction that takes place during the heating of iron salt.
(c) Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Solution 58
(a) Ferrous sulphate.
(b) Decomposition reaction.
(c)
Question 59
A colourless lead salt, when heated, produces a yellow residue and brown fumes.
(a) Name the lead salt.
(b) Name the brown fumes.
(c) Write a chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Solution 59
(a) Lead nitrate.
(b) Nitrogen dioxide.
(c)
Question 60
When hydrogen burns in oxygen, water is formed and when water is electrolysed, then hydrogen and oxygen are produced. What type of reaction takes place:
(a) In the first case?
(b) In the second case?
Solution 60
(a) Combination reaction.
(b) Decomposition reaction.
Question 61
A strip of metal X is dipped in a blue coloured salt solution YSO4. After some time, a layer of metal Y from the salt solution is formed on the surface of metal strip X. Metal X is used in galvanisation whereas metal Y is used in making electric wires. Metal X and metal Y together form an alloy Z.
(a) What could metal X be?
(b) What could metal Y be?
(c) Name the metal salt YSO4
(d) What type of chemical reaction takes place when metal X reacts with salt solution YSO4? Write the equation of the chemical reaction involved.
(e) Name the alloy Z.
Solution 61
(a) Zinc (Zn)
(b) Copper (Cu)
(c) Copper sulphate (CuSO4)
(d) Displacement reaction;
CuSO4 (aq) + Zn (s) ![]() ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
(e) Brass
Question 62
When a black metal compound XO is heated with a colourless gas Y2, then metal X and another compound Y2O are formed. Metal X is red-brown in colour which does not react with dilute acids at all. Gas Y2 can be prepared by the action of a dilute acid on any active metal. The compound Y2O is a liquid at room temperature which can turn anhydrous copper sulphate blue.
(a) What do you think is metal X?
(b) What could be gas Y 2?
(c) What is compound XO?
(d) What is compound Y2O?
(e) Write the chemical equation of the reaction which takes place on heating XO with Y2.
(f) What type of chemical reaction is illustrated in the above equation?
Solution 62
(a) Copper (Cu)
(b) Hydrogen (H2)
(c) Copper oxide (CuO)
(d) Water (H2O)
(e) CuO + H2 ![]() Cu + H2O
Cu + H2O
(f) Displacement reaction (which is also a redox reaction).
Question 63
A metal X forms a water soluble salt XNO3. When an aqueous solution of XNO3 is added to common salt solution, then a white precipitate of compound Y is formed alongwith sodium nitrate solution. Metal X is said to be the best conductor of electricity and it does not evolve hydrogen when put in dilute hydrochloric acid.
(a) What is metal X ?
(b) What is salt XNO3?
(c) Name the compound Y.
(d) Write the chemical equation of the reaction which takes place on reacting XNO3 solution and common salt solution giving the physical states of all the reactants and products.
(e) What type of chemical reaction is illustrated by the above equation?
Solution 63
(a) Silver (Ag)
(b) Silver nitrate (AgNO3)
(c) Silver chloride (AgCl)
(d) AgNO3(aq) + NaCl (aq) ![]() AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq)
AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq)
(e) Double displacement reaction.
Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise 50
Question 64
Two metals X and Y form the salts XSO4 and Y2SO4, respectively. The solution of salt XSO4 is blue in colour whereas that of Y2SO4 is colourless. When barium chloride solution is added to XSO4 solution, then a white precipitate Z is formed along with a salt which turns the solution green. And when barium chloride solution is added to Y2SO4 solution, then the same white precipitate Z is formed along with colourless common salt solution.
(a) What could the metals X and Y be?
(b) Write the name and formula of salt XSO4.
(c) Write the name and formula of salt Y2SO4.
(d) What is the name and formula of white precipitate Z?
(e) Write the name and formula of the salt which turns the solution green in the first case.
Solution 64
(a) Metal X : Copper; Metal Y : Sodium
(b) Copper sulphate, CuSO4
(c) Sodium sulphate, Na2SO4
(d) Barium sulphate, BaSO4
(e) Copper chloride, CuCl2
Question 65
A red-brown metal X forms a salt XSO4. When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through an aqueous solution of XSO4, then a black precipitate of XS is formed along with sulphuric acid solution.
(a) What could the salt XSO4 be?
(b) What is the colour of salt XSO4?
(c) Name the black precipitate XS.
(b) By using the formula of the salt obtained in (a) above, write an equation of the reaction which takes place when hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through its aqueous solution.
(e) What type of chemical reaction takes place in this case?
Solution 65
(a) Copper sulphate.
(b) Blue colour.
(c) Copper sulphide.
(d) CuSO4 (aq) + H2S (g) ![]() CuS (s) + H2SO4 (aq)
CuS (s) + H2SO4 (aq)
(e) Double displacement reaction.
Question 66
When a strip of red-brown metal X is placed in a colourless salt solution YNO3 then metal Y is set free and a blue coloured salt solution X(NO3)2 is formed. The liberated metal Y forms a shining white deposit on the strip of metal X.
(a) What do you think metal X is?
(b) Name the salt YNO3.
(c) What could be metal Y?
(d) Name the salt X(NO3)2
(e) What type of reaction takes place between metal X and salt solution YNO3?
Solution 66
(a) Copper.
(b) Silver nitrate.
(c) Silver.
(d) Copper nitrate.
(e) Displacement reaction.
Question 67
A metal salt MX when exposed to light splits up to form metal M and a gas X2. Metal M is used in making ornaments whereas gas X2 is used in making bleaching powder. The salt MX is itself used in black and white photography.
(a) What do you think metal M is?
(b) What could be gas X2?
(c) Name the metal salt MX.
(d) Name any two salt solutions which on mixing together can produce a precipitate of salt MX.
(e) What type of chemical reaction takes place when salt MX is exposed to light? Write the equation of the reaction.
Solution 67
(a) Silver.
(b) Chlorine.
(c) Silver chloride.
(d) Silver nitrate and Sodium chloride.
(e) Decomposition reaction;
Write the Equation for the Reaction That Occurs When Methanol Is Dissolved in Water
Source: https://www.topperlearning.com/lakhmir-singh-and-manjit-kaur-solutions/cbse-class-10-chemistry/lakhmir-singh-and-manjit-kaur-chemistry/chemical-reactions-and-equations
0 Response to "Write the Equation for the Reaction That Occurs When Methanol Is Dissolved in Water"
Post a Comment